Investigating The Efficacy Of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe)
“SAMe controls many vital hepatic functions as well as the response to liver injury. A very positive review which can encourage further studies and the use of SAMe in liver health disorders” said Lorena Carboni, Product Manager of the branded S-adenosylmethionine Adonat® of Gnosis by Lesaffre.
This is the first systematic review, investigating the efficacy of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) within the early weeks of treatment in adults with intrahepatic cholestasis (IHC). Noureddin M. et al.Early treatment efficacy of S-adenosylmethionine in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis: A systematic review. World J Hepatol.
Data from both randomized and non-randomized studies suggest that SAMe improves some biochemical liver parameters and symptoms of cholestasis within 2 weeks, with further improvements observed in some studies after 4 and 8 weeks of treatment.
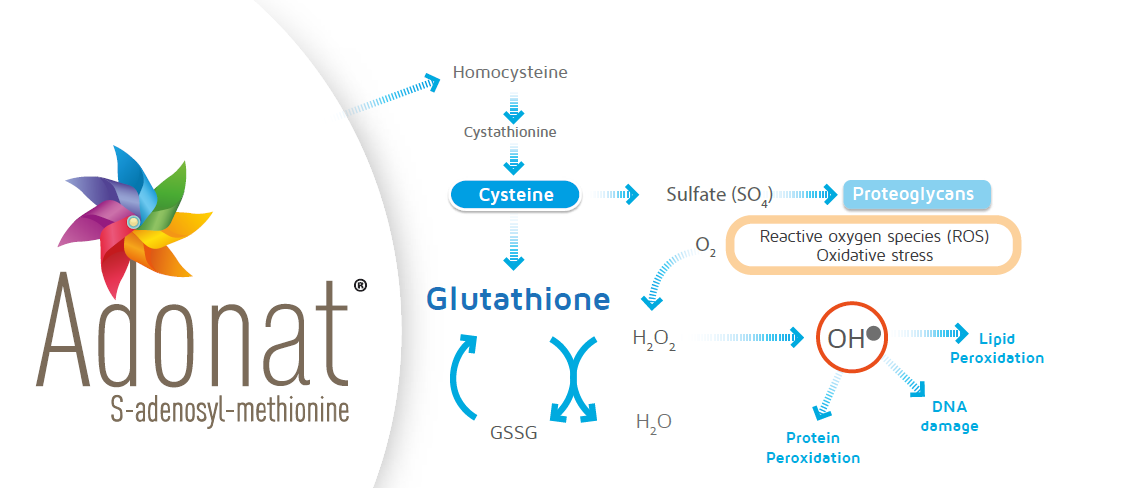
IHC is the impairment of bile formation or bile flow resulting from hepatocellular functional defects or obstructive lesions of the intrahepatic biliary tract. It is associated with clinical signs and symptoms such as pruritus, jaundice, and fatigue, which may subsequently be associated with depression, autonomic dysfunction, and sleep disturbances. SAMe is a natural compound, synthesized and metabolized mainly by the liver via multiple pathways; it is likely that exogenous SAMe is rapidly metabolized, improving overall liver metabolic homeostasis.
Discover more about Adonat® and stay updated through our Newsletter system to receive more info on this specific subject.
Deep Dive Into SAMe
Research studies over the past five decades have unequivocally established the importance of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe). An endogenously produced compound that plays a critical role in cellular metabolism and function, SAMe is second only to ATP as the most important molecule in cell biology.